Here’s your complete e-invoice guideline in 2024! E-Invoicing is mandatory implementation, officially announced by Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM).
As a part of digital transformation, soon all taxpayer businesses in Malaysia, especially high annual turnover is required to implement e-invoicing (electronic invoicing) into their business.
Here, so you’ll find plenty of practical tips in this fresh guide.
Let’s get started!
In this article:
- What e-invoice is
- Implementation of e-invoice in Malaysia
- E-Invoice specific guideline
- What are the requirements for e-Invoice and e-Invoice guideline
What is e-Invoicing?
An e-invoice in Malaysia is a digital record of a transactional exchange between a seller (supplier) and a purchaser (buyer) that is submitted and validated through a government portal in real-time for recordkeeping purposes.
The einvoice Malaysia contains 55 fields detailing various aspects of the transaction, such as seller and buyer details, information, item description, quantity, price, tax, total amount, and payment details.
Once successfully validated, the e-invoice is assigned a Unique Identification Number (UIN) and a QR Code, both generated by the MyInvois Portal, which enables online validation of the invoice.
This system is part of Malaysia's broader initiative to digitize tax administration and improve efficiency in invoicing and tax reporting.
E-Invoice implementation timeline
The e-invoicing implementation timeline in Malaysia from 2024-2025 is as follows:
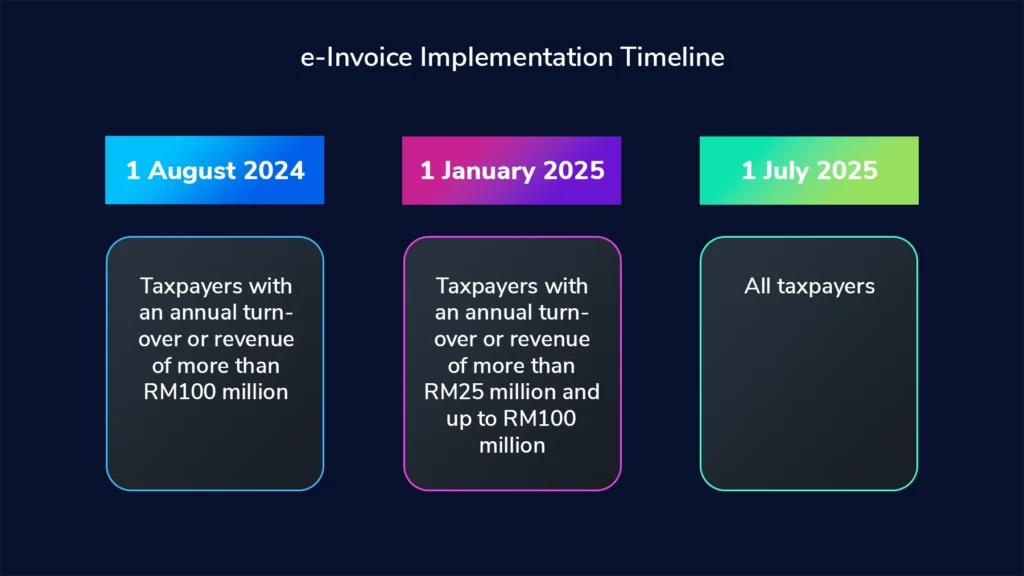
- May 1, 2024: Start of the pilot phase for e-invoicing.
- August 1, 2024: Mandatory e-invoicing for taxpayers with an annual turnover of more than MYR 100 million.
- January 1, 2025: Mandatory e-invoicing for taxpayers with an annual turnover between MYR 25 million and MYR 100 million.
- July 1, 2025: Mandatory e-invoicing for all other taxpayers.
This phased (implementation dates of Malaysia e-invoice) approach aims to ensure a smooth transition to electronic invoicing across various business sectors in Malaysia including sub-con and sole proprietorship business.
But why e-invoice?
The benefits of einvoice Malaysia are numerous and align with the government's objectives to enhance the digital economy and improve tax administration. Here are the key benefits of implementing e-invoicing and the rationale behind making it mandatory:
Benefits of E-Invoicing in Malaysia
- Unified Invoicing: E-invoicing streamlines the creation and submission of invoices, allowing for automation in data entry. This reduces the time and effort required to generate invoices.
- Integrated Tax Filing: E-invoicing ensures that tax reporting is efficient and accurate. The integration facilitates seamless compliance with tax regulations, reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Streamlined Operations: By digitizing the invoicing process, businesses can significantly increase their operational efficiency. This leads to resource savings in managing tax compliance and related activities.
- Improved Cash Flow: E-invoicing minimizes billing errors, speeds up payment cycles, and reduces disputes between buyers and sellers. This leads to better cash flow management for businesses.
- Digitized Reporting: E-invoicing aligns financial reporting with digital standards, making it easier for businesses to maintain compliance and generate necessary reports for stakeholders.
- Paperless Invoicing: The transition to e-invoicing eliminates the need for paper, contributing to environmental sustainability and preventing tax leakage through improved tracking of transactions.
Rationale for making e-Invoicing mandatory
- Modernization of Tax Administration: The Malaysian government aims to digitize and modernize tax administration, making it more efficient and transparent. Mandatory e-invoicing is a step towards achieving this goal.
- Enhanced Compliance and Reporting: By mandating e-invoicing, the government can ensure better compliance with tax regulations and facilitate real-time monitoring of transactions, which helps in reducing tax evasion.
- Boosting the Digital Economy: Mandating e-invoicing is aligned with broader efforts to promote the digital economy in Malaysia. It encourages businesses to adopt digital technologies, fostering innovation and economic growth.
- Improving Data Accuracy: E-invoicing reduces manual data entry errors, promoting accuracy in transaction records and financial reporting. This is essential for effective tax collection and auditing.
- Facilitating Economic Growth: The increased efficiency and transparency afforded by e-invoicing are expected to stimulate economic growth by making it easier for businesses to operate in a digital environment.
Now that we know that the mandatory implementation of e-invoicing in Malaysia is designed to enhance operational efficiency, improve tax compliance, support the digital economy, and promote sustainable practices—all contributing to a more robust economic framework.
Types of e-invoicing in Malaysia
Here in Malaysia, there are several types of e-invoices (electronic invoice) as part of the transition from traditional invoicing methods to a more efficient digital system. The key types include:
- Standard e-Invoice: This is the basic form of e-invoice that represents a digital transaction between a supplier and a buyer. It must comply with the digital format specified by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) to ensure proper processing (typically in XML or JSON formats) as part of their e-invoicing regulations.
- Consolidated e-Invoice: Suppliers will be required to aggregate normal receipts or invoices issued to end consumers and issue a consolidated e-invoice. This type will support the transactions made with end consumers and is aimed at simplifying record-keeping for businesses.
- Credit Notes and Debit Notes: As part of the e-invoicing framework, electronic versions of credit notes and debit notes will also be utilized, allowing for adjustments to be easily recorded and processed digitally.
- Validated e-Invoice: Once an e-invoice is submitted through the MyInvois Portal and successfully validated, it will contain a Unique Identification Number (UIN) and a QR Code. This allows for online validation of the invoice, enhancing verification processes for both suppliers and buyers.
As the implementation of e-invoicing in Malaysia progresses, businesses will be required to adapt to these different types of e-invoices to streamline their invoicing processes and comply with regulatory e-invoicing requirements.
Overview of the e-Invoicing model in Malaysia
To facilitate transition to e-Invoice, taxpayers can select the most suitable mechanism to transmit e-Invoices to IRBM, based on their business requirements and specific situation.
So far, there are two (2) options for the e-Invoice transmission mechanisms for taxpayers' selection, based on LHDN website, either by Software Development Kit or Portal by IRBM:
Direct upload to Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) portal
The MyInvois Portal, hosted by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM), serves as a key mechanism for e-Invoicing, designed to facilitate compliance for taxpayers mandated to adopt electronic invoicing.
This user-friendly platform is available to all taxpayers at no cost, making it particularly suitable for micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) that may not have extensive technological resources.
Through the MyInvois Portal, businesses can easily generate, submit, and validate e-Invoices in real-time, ensuring they meet the necessary standards and criteria set forth by the IRBM.
While the portal provides a straightforward solution for businesses with lower transaction volumes, it may be less efficient for those with high volumes of data, who might benefit from the more advanced Application Programming Interface (API) option.
Overall, the MyInvois Portal aims to streamline the e-Invoicing process, supporting taxpayers in their transition to a digital invoicing framework.
Using the Software Development Kit for invoice submission
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) has introduced a Software Development Kit (SDK) specifically designed for e-invoicing as part of the upcoming e-invoicing mandate set to take effect in August 2024.
This SDK serves as a comprehensive resource for developers, providing a collection of tools, libraries, and application programming interfaces (APIs) that facilitate the integration of existing e-invoice system with the MyInvois system.
The SDK includes detailed development guidelines, enabling businesses and service providers to effectively implement e-invoicing processes.
Additionally, it features a FAQ section that addresses common queries regarding integration with the MyInvois system. There are few versions so far, including beta version of the SDK releases.
The e-invoice software development kit (SDK) aims to streamline the transition to e-invoicing with high annual turnover and transaction volume, ensuring compliance and enhancing operational efficiency for users.
Features of the CTC Electronic Invoicing in Malaysia
1. Clear Invoice Model:
The CTC (Continuous Transaction Control) electronic invoicing model mandates the inclusion of specific fields in every invoice submitted to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM). This ensures standardization and compliance with regulatory requirements.
2. Real-Time Clearance:
Invoices submitted through the CTC system will undergo a real-time clearance process. This means that businesses will receive immediate validation of their invoices, allowing for faster processing and fewer discrepancies.
3. Data Accuracy and Integrity:
Robust data integration processes are set up to ensure that the information in invoices is accurate and consistent. This minimizes the risk of errors that can lead to rejections or complications in transactions.
4. User-Friendly Interface:
The CTC system is designed to be user-friendly, making it easier for businesses to transition to electronic invoicing. This includes intuitive navigation and support for integration with existing accounting systems.
5. Proactive Monitoring:
With inbuilt monitoring mechanisms, the CTC system provides businesses with real-time visibility into their invoicing activities. This allows for the proactive identification and resolution of issues, enhancing operational efficiency.
6. Cost-Effectiveness:
The implementation of the CTC electronic invoicing model is geared towards providing cost-effective solutions for businesses, reducing the overhead associated with traditional invoicing methods and minimizing errors that can lead to financial penalties.
7. Compliance with Regulatory Changes:
The CTC system is designed to align with Malaysia's evolving regulatory landscape for e-invoicing, ensuring that businesses remain compliant with the Inland Revenue Board's guidelines, e-invoicing rules and requirements.
8. Interoperability:
The CTC framework promotes interoperability, allowing for seamless transactions between various business systems and the MyInvois Portal, making it easier for businesses to interact with the IRBM and each other.
9. Scalability:
The CTC electronic invoicing model is scalable, accommodating businesses of different sizes and sectors, thereby ensuring that all taxpayers can transition smoothly to the new e-invoicing mandate by the IRBM.
10. Support for Multiple Transaction Types:
The CTC model accommodates a variety of transaction types, including B2B, B2C, and B2G transactions, ensuring that all business operations can benefit from electronic invoicing.
These features collectively enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and transparency of financial operations within the Malaysian business landscape as the implementation of electronic invoicing takes effect.
How to register and implement e-invoicing in Malaysia
By far einvoice Malaysia is a game changer for SMEs. We've learned about e-invoicing guideline, e-invoice documents and its benefits. It's maybe now the time for you to digitalize your business ecosystem.
Below are current practices of step-by-step guide on how to register and implement them into your company:
Step 1: Understand the Requirements
- Review Compliance Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the guidelines set by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) regarding electronic invoicing. Make sure you understand the mandatory requirements and the phased implementation timeline.
- Determine Your Business’s Turnover: Identify your business's annual turnover or revenue to know when you will be required to comply with the e-invoicing mandate. Businesses with an annual turnover of more than MYR 100 million will start e-invoicing from August 1, 2024.
Step 2: Choose an E-Invoicing Solution
- Select an E-Invoicing Provider: Choose a compliant e-invoicing solution provider. Look for solutions accredited by the Malaysian Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC).
- Understand the E-Invoicing Models: Decide whether your business will use the MyInvois Portal or an API integration with your business system for generating e-invoices.
Step 3: Register with MyInvois Portal
- Create an Account: Register for an account on the MyInvois Portal, which is the platform used to generate and submit electronic invoices to IRBM.
- Provide Necessary Information: Fill in the required details, such as your business registration number and relevant contact information.
Step 4: Integrate E-Invoicing System
- System Integration: If you opt for the API model, work with your IT team or service provider to integrate the e-invoicing API into your existing accounting or invoicing software.
- Testing: Conduct tests to ensure that the integration works correctly and that invoices can be generated and submitted seamlessly.
Step 5: Train Your Staff
- Provide Training: Train relevant staff on the new e-invoicing processes and how to use the MyInvois Portal or the selected API integration.
- Create SOPs: Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for generating, submitting, and managing e-invoices.
Step 6: Start Generating E-Invoices
- Create and Submit E-Invoices: Begin generating e-invoices for your transactions as per the requirements. Ensure each e-invoice includes the Unique Identification Number (UIN) and QR Code generated by the MyInvois Portal for validation.
- Maintain Records: Retain electronic invoices for a minimum of seven years as required by Malaysian law.
Step 7: Stay Informed
- Monitor Updates: Keep an eye on any further guidance or updates from IRBM regarding e-invoicing guideline, particularly regarding disbursements and reimbursements.
- Compliance Check: Regularly review your e-invoicing processes to ensure compliance with any changing regulations.
Step 8: Prepare for Future Phases
- Plan for Phased Implementation: If your turnover is below MYR 100 million, prepare for the later phases of mandatory e-invoicing, which will begin in January 2025 for businesses with turnover exceeding MYR 25 million.
In conclusion, the introduction of e-invoicing in Malaysia marks a significant step towards enhancing business efficiency and compliance with tax regulations. By digitizing the invoicing process, companies can streamline operations, improve cash flow, and reduce errors.
Boost your digital potentials today
With our digital agency, you can get corporate website and digital marketing you need to grow your business. Effectively improve your digital potentials.
- Website Design: For you to retain more corporate clients.
- SEO: Rank your website higher on Google search and profile on Google Maps
- Content Marketing: Get high-quality post for your social media and website for brand awareness.
- Managed Google Ads: Show your website in front of potentials who are looking for the services and products you sell. Instantly with paid ads.



